CDRouter USP User Guide
Introduction
User Services Platform
The User Services Platform (USP), as defined in Broadband Forum TR-369, is the next generation of the TR-069 protocol. It’s lighter weight, more flexible and adds some powerful new features.
In the TR-069 domain, all messages are transported over HTTP or HTTPS. In some cases, XMPP is used for connection requests. In contrast, USP has far more combinations to test. Messages can be transported over WebSocket, MQTT (version 3.1.1 or 5) or STOMP, each with optional encryption. Additionally, each exchange between endpoints can optionally use a session context, optionally encrypt the USP payload and optionally segment payloads at the USP layer.
The CDRouter USP expansion adds USP test capabilities to CDRouter, allowing you to test under all the conditions mentioned in a simple, easy to configure way.
The full specification for USP can be found at usp.technology.
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Endpoint | An Endpoint is a termination point for a Message. |
| Endpoint ID | A unique identifier assigned to a USP endpoint. |
| Agent | An Agent is an Endpoint that exposes Service Elements to one or more Controllers. |
| Controller | A Controller is an Endpoint that manipulates Service Elements through one or more Agents. |
| Service Elements | Named objects and parameters maintained by the Agent that allow it to be managed by the Controller. |
| Data Model | The set of Service Elements defined and supported by the Agent. Data Model specifications are organized in a hierarchy and published as XML documents. |
| Message | USP Protocol requests and responses that allow the Controller to query and modify the Service Elements of the Agent. |
| Record | The USP Record carries a USP Message as its payload. It specifies the source and destination of the Endpoints as well as metadata to provide integrity protection, payload security and delivery of fragmented Messages. |
| MTP | Message Transfer Protocol (MTP), the protocol used to encapsulate and transport USP Records between Endpoints. |
| Session Context | A set of additional fields in the USP Record that are exchanged between USP endpoints which allow either side to reassemble out of order Records, request retransmission of missed Records, authenticate messages as coming from allowed endpoints and encrypt messages to allow secure communication between Endpoints. |
| Path | A MTP-specific string which is used in the transportation and delivery of USP messages between Endpoints. |
| USP Encryption | A method of encrypting the USP payload with TLS that is available when using session contexts. |
Requirements and License
CDRouter USP is available for CDRouter 11.0 and newer releases only.
Licensing
CDRouter USP is a licensed expansion that must be purchased from QA Cafe. For information on upgrading a license to include CDRouter USP or any other expansions, please contact sales@qacafe.com.
CDRouter will report the status of all available expansions during the installation
process and during start-up. To verify that CDRouter USP is enabled on a system,
run the command cdrouter-cli -info as root and look for the line USP is
enabled, as shown below. If this line is present, CDRouter USP is enabled
and ready to use.
$ cdrouter-cli -info
Starting /usr/cdrouter/bin/cdrouter-cli Thu Mar 15 11:12:22 EDT 2018
Copyright (c) 2001-2018 by QA Cafe
Version 11.0 build 0 (b1081f6e0 master), built 2018-03-14 10:51:06 by nightly@cdr-forge6.lan (x86_64)
OS: CentOS Linux 7.4.1708 (4.4.87-1.el7.qacafe.x86_64)
CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-7600K CPU @ 3.80GHz
Loaded modules from: '/usr/cdrouter/tests'
Start command: /usr/cdrouter/bin/cdrouter-cli -info
System ID: b2d8619a16720c7c3fc0835500badc15
Registered to: qacafe
Maintenance, support and upgrades until: 2085-01-01
Test suite: cdrouter
Multiport is enabled
IPv6 is enabled
Storage is enabled
IKE is enabled
TR69 is enabled
TR69-EDM is enabled
Nmap is enabled
BBF.069 is enabled
SNMP is enabled
Performance is enabled
ICS is enabled
DOCSIS is enabled
USP is enabled
Test Methodology
Overview
The network topology of USP endpoints is highly flexible by design. In CWMP the only topology is one in which the TR-069 client is either a gateway or behind a gateway on the LAN side of a network and a single ACS sits somewhere on the internet. While this configuration is still valid in USP, it is by no means the only option. The USP standard was designed not only from the perspective of organizations controlling their products remotely but also from consumers controlling the products in their home. For this reason USP is designed to enable the configuration of an agent from one or more controllers that exist within the same network.
CDRouter is capable of testing common USP network topologies. CDRouter’s USP controller will always be configured on CDRouter’s simulated WAN, but a directly connected agent can be tested using any of the MTPs. Additionally with WebSocket and STOMP, an agent can be placed behind a gateway. For all USP testing CDRouter’s full suite of network address provisioning mechanisms are available for use.
The USP expansion supports all MTPs with or without TLS over both IPv4 and IPv6, and with or without USP layer encryption. All the defined message types are supported as well as segmentation of both USP records and TLS records at the USP layer.
The following MTP, MTP encryption, USP encryption, IP version options are testable using the USP CDRouter expansion:
| MTP | Supported MTP Encryption | Supported USP Encryption | Supported IP Versions | Supports USP Segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WebSocket | TLS or None | TLS v1.2 or None | IPv4 or IPv6 | Yes |
| STOMP | TLS or None | TLS v1.2 or None | IPv4 or IPv6 | Yes |
| MQTT (v5) | TLS or None | TLS v1.2 or None | IPv4 or IPv6 | Yes |
| MQTT (v3.1.1) | TLS or None | TLS v1.2 or None | IPv4 or IPv6 | Yes |
What is not supported:
When using TLS at the USP layer CDRouter uses a certificate that does not
include the controller’s endpoint ID in the subjectAltName field. This is
because the certificate used by CDRouter’s controller is signed by a trusted CA
and the controller’s endpoint ID is configurable. Additionally CDRouter will not
validate that the subjectAltName of certificates sent by an agent contains the
endpoint ID of the agent. If the agent being tested validates the subjectAltName
in the certificate it receives from the controller this can be overcome by
providing certs for the controller to use by setting uspControllerUSPCertPath
and uspControllerUSPCaCertPath to the
path to a certificate/CA certificate pair that the agent will accept (note that
this may also require setting uspControllerID to match the
endpoint ID in the subjectAltName in the provided certificate).
Initial Setup
CDRouter’s USP controller runs on the WAN interface. This presents three possible setups for testing USP Agents.
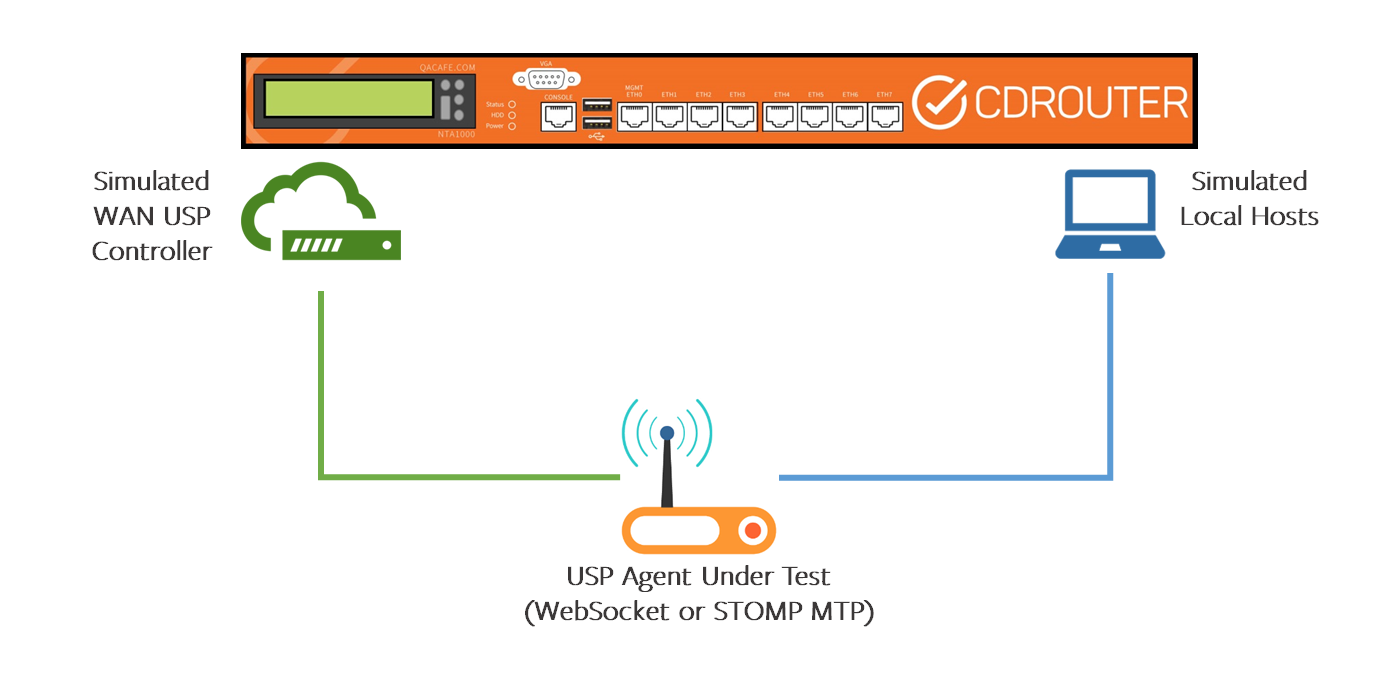
Test Setup #1
If the USP Agent is accessible via the WAN connection on a gateway, the setup is the same as the basic CDRouter test setup for CWMP:
Test Setup #2
If the USP Agent is on an end-device, you can use an additional gateway as part of your test setup.
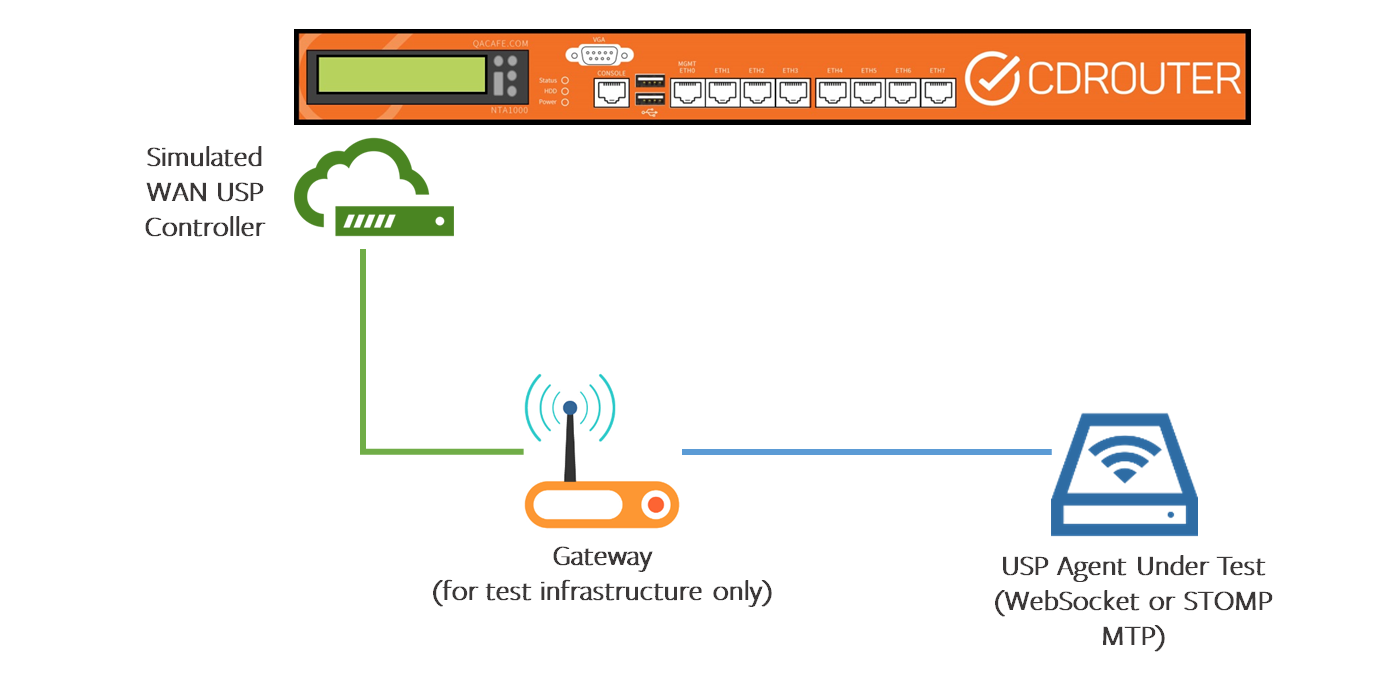
Test Setup #3
Alternatively, you can connect a USP Agent directly to CDRouter’s WAN port and run your testing without the LAN port configured.
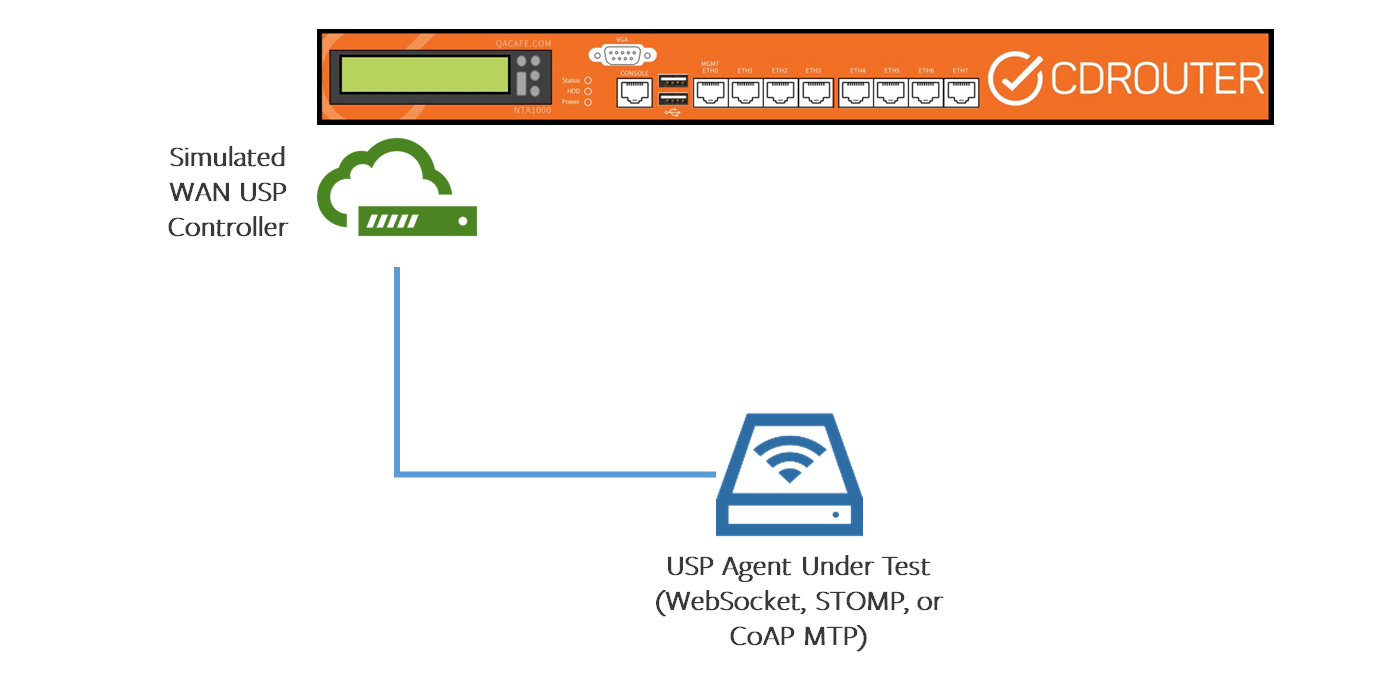
Configuration
To configure CDRouter for USP testing, first determine your agent’s configuration by examining its data model.
This section covers the most common USP configuration scenarios and testvar settings needed to allow the USP agent (DUT) to connect to CDRouter’s USP Controller.
Example configurations for each MTP and the corresponding agent parameters are provided in the MTP Configuration Examples section.
Enabling USP
In order to run any of the USP test cases, CDRouter’s USP controller must be enabled.
This is done by setting supportsUSP to “yes”.
testvar supportsUSP yes
Controller Configuration
The “CDRouter USP Expansion” contains all of the testvars needed to configure CDRouter’s USP controller so that it can communicate with the agent (DUT). Below is a list of the most frequently used testvars for all configurations.
(Some of these testvars may not be needed for certain types of environments and may be ignored.)
testvar supportsUSP yes
testvar uspControllerID proto::controller-id
testvar uspControllerIpMode ipv4-only
testvar uspControllerIpv4 6.0.0.2
testvar uspControllerIpv6 6000::2
testvar uspControllerDomain controller.cdroutertest.com
testvar uspControllerPort auto
testvar uspControllerMTP websocket
testvar uspControllerPath /controller-path
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption no
testvar uspControllerUseSessionContext no
testvar uspControllerUSPEncryption no
testvar uspAgentID proto::agent-id
testvar uspAgentPort auto
testvar uspAgentPath /agent-path
TLS encryption is disabled by default but may be enabled at both the MTP and USP layers.
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption yes
testvar uspControllerMTPCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com.pem
testvar uspControllerMTPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com-ca.pem
testvar uspControllerUseSessionContext yes
testvar uspControllerUSPEncryption yes
testvar uspControllerUSPCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com.pem
testvar uspControllerUSPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com-ca.pem
Each of the CDRouter testvars are explained in more detail below.
Controller and Agent Endpoint ID
Both the USP controller and agent have a unique identifier that is used
to exchange messages with each other. These identifiers are set by the
uspControllerID and uspAgentID testvars,
and must match the corresponding “EndpointID” parameters in the agent’s
data model.
testvar uspControllerID proto::controller-id
testvar uspAgentID proto::agent-id
Controller’s Domain Name and IP Address
The USP controller can be configured to run over IPv4 or IPv6. This is done by
setting uspControllerIpMode to either “ipv4-only” or
“ipv6-only”.
Once an IP version has been selected, the controller’s IP address can be
configured by setting uspControllerIpv4 for an IPv4 address
testvar uspControllerIpMode ipv4-only
testvar uspControllerIpv4 6.0.0.2
or uspControllerIpv6
for an IPv6 address.
testvar uspControllerIpMode ipv6-only
testvar uspControllerIpv6 6000::2
CDRouter will also add a DNS entry mapping the configured IP address
of the controller to a domain name. To specify the domain named used set uspControllerDomain
to the desired domain name.
MTP Protocol
The agent and controller must be configured to use the same Message Transfer Protocol (MTP). CDRouter has support for the following MTPs:
WebSocket, STOMP, MQTTv5, MQTTv3.1.1
To configure a specific MTP, set uspControllerMTP to:
stompwebsocketmqtt(for MQTTv5)mqttv3(for MQTTv3.1.1).
testvar uspControllerMTP websocket
MTP Port
The uspControllerPort and uspAgentPort
testvars specify the TCP port number where the controller and agent
listen for incoming connections.
testvar uspControllerPort auto
testvar uspAgentPort auto
Each testvar has a default value of “auto” that allows CDRouter to automatically use the correct well-known port reserved for the selected MTP protocol, depending on whether TLS encryption is enabled or not. The port number can also be manually set to explicitly match the port used in the DUT’s configuration.
Well-known MTP Ports
| MTP Protocol | Unencrypted | With TLS encryption |
|---|---|---|
| WebSocket | 80 | 443 |
| STOMP | 61613 | 61614 |
| MQTT | 1883 | 8883 |
MTP Path
Each MTP requires an additional parameter to facilitate message delivery between USP Endpoints. Different MTPs use different terms for this identifier—such as Path, Destination, or Topic.
In CDRouter, the uspControllerPath and uspAgentPath testvars represent this parameter for the Controller and Agent, respectively.
testvar uspControllerPath /controller-path
testvar uspAgentPath /agent-path
The table below lists the parameter each testvar corresponds to for every available MTP.
- MTP Path Parameter Names:
MTP Testvar Agent Parameters WebSocket uspAgentPathuspControllerPathDevice.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.PathDevice.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.PathSTOMP uspAgentPathuspControllerPathDevice.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.STOMP.DestinationDevice.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.STOMP.DestinationMQTT uspAgentPathuspControllerPathDevice.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.MQTT.ResponseTopicConfiguredDevice.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.MQTT.Topic
STOMP and MQTT Authentication
When using STOMP or MQTT as the MTP, CDRouter will simulate a STOMP/MQTT
broker server to accept connections from the DUT. The uspControllerUsername and uspControllerPassword
testvars are used to specify the login credentials that the agent must
use to authenticate with the broker server.
Additionally, CDRouter’s STOMP server can be
configured to only accept specific values in the “host” header of the STOMP
frame by setting uspControllerHost to the value the agent will
provide.
Enabling TLS Encryption
TLS is supported at both the MTP and USP message layers.
Default TLS Certificates
CDRouter is shipped with a default TLS certificate that is valid for
any host in the "cdroutertest.com" domain. The certificate is signed
by a commercial Certificate Authority, so most devices should be able
to validate it without any additional configuration.
Set uspControllerMTPEncryption or
uspControllerUSPEncryption to “yes” to enable TLS
encryption at the MTP or USP message layer, respectfully. CDRouter will
automatically use its default certificates to establish the connection
with the agent.
testvar uspControllerDomain "controller.cdroutertest.com"
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption yes
testvar uspControllerMTPCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com.pem
testvar uspControllerMTPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com-ca.pem
testvar uspControllerUSPEncryption yes
testvar uspControllerUSPCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com.pem
testvar uspControllerUSPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter/tests/wildcard.cdroutertest.com-ca.pem
uspControllerMTPCertPath specifies the file containing the USP controller certificate and associated private key used to encrypt the TLS connection.
uspControllerMTPCaCertPath indicates a file containing the certificates of any Certificate Authorities that may be needed to validate the certificate chain.
Custom TLS Certificates
You can configure the controller to use your own TLS certificates instead of CDRouter’s default ones. This is useful if your agent is required to connect to controllers from a specific domain.
A valid controller certificate matching the controller’s fully-qualified domain name (FQDN), as well as a corresponding private key must be provided in order for CDRouter’s controller to establish a TLS connection successfully.
Steps to configure private TLS certificates:
-
Upload a file containing both the controller certificate in PEM format and its associated private key to the
/usr/cdrouter-data/customdirectory of your NTA platform. Set theuspControllerMTPCertPathto the full pathname of the file. -
Upload a separate file containing any Certificate Authority certificates needed to validate the controller certificate, and set the
uspControllerMTPCaCertPathto its pathname. -
Set the
uspControllerDomaintestvar to a fully-qualified domain name that matches the “Common Name” (CN) field of your controller certificate. CDRouter’s DNS server will automatically resolve this domain name to the controller’s IPv4/IPv6 address.If the CN field of your certificate uses a wildcard domain name (eg. “*.example.com”),
uspControllerDomainshould be set to an arbitrary hostname within that domain (eg. “controller.example.com”).
testvar uspControllerDomain "mycontroller.company.com"
testvar uspControllerMTPCertPath /usr/cdrouter-data/custom/mycert.pem
testvar uspControllerMTPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter-data/custom/mycert-ca.pem
To specify the port the controller should listen on for incoming connections, set
uspControllerPort to the desired port number. Setting this
testvar to “auto” will cause CDRouter to use the default port for the MTP based
off the values of uspControllerMTP and uspControllerMTPEncryption.
Session Contexts and USP Layer Encryption
By default the USP controller will not use Session Contexts, nor will it use USP level security.
To enable the use of session contexts, set the
uspControllerUseSessionContext testvar to “yes”. This
will require the agent to support session contexts as well in order for
testing to proceed.
To enable USP level security with TLS message encryption, you must enable
session contexts and also set uspControllerUSPEncryption
to “yes”.
testvar uspControllerUseSessionContext yes
testvar uspControllerUSPEncryption yes
CDRouter’s USP controller will also use the Comodo signed certs by default for
USP layer encryption. If a different set of certificates should be used, it
can be configured by setting uspControllerUSPCertPath and uspControllerUSPCaCertPath
to the appropriate paths.
testvar uspControllerUSPCertPath /usr/cdrouter-data/custom/mycert.pem
testvar uspControllerUSPCaCertPath /usr/cdrouter-data/custom/mycert.pem
Agent IP Address
If the IP address of the USP agent is different from the primary
address of the DUT (wanIspAssignIp or ipv6WanIspAssignIp), you can configure it using uspAgentIpv4 or
uspAgentIpv6, depending on the value of
uspControllerIpMode. Otherwise, leave these testvars set to “auto”.
testvar uspAgentIpv4 auto
testvar uspAgentIpv6 auto
Setting the Controller’s Default USP Behavior
CDRouter’s default behavior when it starts a new USP session can be configured.
By default, the USP controller will wait 30 seconds for an agent to reply to a message.
This can be configured by setting uspMessageTimeout.
testvar uspMessageTimeout 90
Agent Configuration
The USP testvars settings in your config file must match the settings in the agent’s data model.
Each of the testvars described in “Controller Configuration” corresponds to a specific configuration parameter setting in the agent’s data model that allows it to locate and connect to the controller.
The USP agent is typically configured by modifying management parameters in its data model.
The specific CLI commands or tools used to configure the agent are device dependent.
Examples CLI interfaces include:
obuspaubus-cli
OB-USP-Agent
The Broadband Forum’s OB-USP-Agent is a popular open-source User Services Platform (USP) agent reference implementation. It enables communication and control of connected devices by utilizing parameters from the Device:2 data model.
For a detailed overview and initial setup steps, refer to the OB-USP-Agent Quick Start Guide.
Agent Data Model
An agent may have multiple USP agent instances managed by different
controllers. To configure your DUT’s agent to work with CDRouter’s
controller, you must either create a new instance of each of the objects
listed above, or reconfigure an existing pair of instances. Be sure
to note the instance numbers ({i}) of any parameter paths your DUT
is using.
Two object branches are defined in the data model to configure the DUT’s USP connections to a controller:
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.– This branch defines how the agent receives messages.Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.– This branch defines the controller that the agent will connect to.
Agent Parameters
Device.LocalAgent.EndpointID
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.Enable
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.Protocol
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Path
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryption
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Destination
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Reference
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.MQTT.ResponseTopicConfigured
Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.MQTT.Reference
Controller Parameters
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.Enable
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.EndpointID
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.E2ESession.SessionMode
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.Enable
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.Protocol
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Host
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Path
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryption
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Destination
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Reference
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.MQTT.Topic
Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.MQTT.Reference
The STOMP and MQTT protocols also have branches that are referenced by the agent connection instances defined above when these MTP protocols are in use:
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.
When the agent is configured to use STOMP or MQTT, CDRouter will simulate the broker server used to forward messages to the controller.
STOMP Broker Parameters
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Enable
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Host
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Port
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Username
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Password
Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.EnableEncryption
MQTT Broker Parameters
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Enable
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.ProtocolVersion
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.BrokerAddress
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.BrokerPort
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Username
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Password
Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.TransportProtocol
MTP Configuration Examples
The example configurations below show CDRouter testvars settings with the matching parameters that should be set in the agent’s data model. See “Agent Configuration” for details on modifying parameters in your DUT’s data model.
WebSocket
Unencrypted Connection
-
Agent parameter settings:1
Agent Parameters Device.LocalAgent.EndpointIDproto::agent-id Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.ProtocolWebSocket Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port80 Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Path/agent-path Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryptionfalse Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.EndpointIDproto::controller-id Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.ProtocolWebSocket Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Hostcontroller.cdroutertest.com Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port80 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Path/controller-path Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryptionfalse -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspAgentID proto::agent-id testvar uspAgentPath /agent-path testvar uspControllerID proto::controller-id testvar uspControllerMTP websocket testvar uspControllerPort auto testvar uspControllerPath /controller-path testvar uspControllerUsername qacafe testvar uspControllerPassword qacafe123 testvar uspControllerDomain controller.cdroutertest.com testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption no
TLS Encrypted Connection
TLS configuration is identical to the Unencrypted configuration with the following changes:
-
Agent parameter settings:1
Agent Parameters Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port443 Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryptiontrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.Port443 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.WebSocket.EnableEncryptiontrue -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption yes
STOMP
-
Agent parameter settings:
Agent Parameters Device.LocalAgent.EndpointIDproto::agent-id Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Enabletrue Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Port61613 Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Hostcontroller.cdroutertest.com Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Usernameqacafe Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Passwordqacafe123 Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.EnableEncryptionfalse Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.ProtocolSTOMP Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Destination/agent-path Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.STOMP.ReferenceDevice.STOMP.Connection.{i} 2 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.EndpointIDproto::controller-id Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.ProtocolSTOMP Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.STOMP.ReferenceDevice.STOMP.Connection.{i} 2 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.STOMP.Destination/controller-path -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspAgentID proto::agent-id testvar uspAgentPath /agent-path testvar uspControllerID proto::controller-id testvar uspControllerMTP stomp testvar uspControllerPort auto testvar uspControllerPath /controller-path testvar uspControllerUsername qacafe testvar uspControllerPassword qacafe123 testvar uspControllerDomain controller.cdroutertest.com testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption no
TLS Encrypted Connection
TLS configuration is identical to the Unencrypted configuration with the following changes:
-
Agent parameter settings:1
Agent Parameters Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Port61614 Device.STOMP.Connection.{i}.EnableEncryptiontrue -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption yes
MQTTv5
-
Agent parameter settings:
Agent Parameters Device.LocalAgent.EndpointIDproto::agent-id Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Enabletrue Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.BrokerAddresscontroller.cdroutertest.com Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.ProtocolVersion5.0 Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.BrokerPort1883 Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.TransportProtocolTCP/IP Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Usernameqacafe Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Passwordqacafe123 Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.ProtocolMQTT Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.MQTT.ResponseTopicConfigured/agent-path Device.LocalAgent.MTP.{i}.MQTT.ReferenceDevice.MQTT.Client.{i} 3 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.EndpointIDproto::controller-id Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.Enabletrue Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.ProtocolMQTT Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.MQTT.ReferenceDevice.MQTT.Client.{i} 3 Device.LocalAgent.Controller.{i}.MTP.{i}.MQTT.Topic/controller-path -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspAgentID proto::agent-id testvar uspAgentPath /agent-path testvar uspControllerID proto::controller-id testvar uspControllerMTP mqtt testvar uspControllerPort auto testvar uspControllerPath /controller-path testvar uspControllerUsername qacafe testvar uspControllerPassword qacafe123 testvar uspControllerDomain controller.cdroutertest.com testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption no
TLS Encrypted Connection
TLS configuration is identical to the Unencrypted configuration with the following changes:
-
Agent parameter settings:1
Agent Parameters Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.Port8883 Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.ProtocolTLS -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspControllerMTPEncryption yes
MQTTv3.1.1
The MQTTv3.1.1 configurations are identical to MQTTv5 with the following changes:
Unencrypted and TLS Encrypted Connection
-
Agent parameter settings:
Agent Parameters Device.MQTT.Client.{i}.ProtocolVersion3.{i}.1 -
CDRouter testvar settings:
testvar uspControllerMTP mqttv3
USP Scenario Testing
USP Scenarios are lightweight, custom test scripts you can develop to execute commands from CDRouter’s USP Controller to validate parameters, reboot the DUT and perform other actions.
Details can be found in the USP Scenario Scripting Guide in our Knowledge Base.
USP Profile Testing
Much like CWMP Profile testing, CDRouter is able to perform USP profile tests to ensure a USP agent has correctly implemented all the required parameters of a data model’s profile.
The following profile test modules are available:
- USP_Device2_profile.tcl
- USP_FAPService2_profile.tcl
- USP_StorageService1_profile.tcl
- USP_STBService1_profile.tcl
- USP_VoiceService1_profile.tcl
For each profile, CDRouter defines several generic tests that verify the consistency of the profile:
- Verify all required parameter names are returned using Get
- Verify all required parameters exist using GetSupportedDM
- Verify the read and write status of each parameter using GetSupportedDM
- Verify all writable parameters can be set using Set
- Verify the creation and deletion of all creatable objects using Add and Delete
Configuring Which Profiles are Tested
CDRouter has the ability to skip unsupported profiles automatically after specifying what the agent supports.
The agent’s supported data model can be configuring using the testvar uspSupportedDataModel,
which supports several different options. Setting this
testvar to the keyword all indicates that the agent supports every profile
from all officially defined USP data models:
testvar uspSupportedDataModel "all"
A list of top level data models can be specified to indicate that all the profiles in only those data models are supported:
testvar uspSupportedDataModel {Device:2.13 VoiceService:2.0}
A DeviceSummary string as defined in Section 3.7 of TR-106 can also be
specified:
testvar uspSupportedDataModel {Device:2.13[](Baseline:2),VoiceService:2.0[1](Baseline:1)}
Or:
testvar uspSupportedDataModel {Device:2.15[](IPInterface:1,WiFiRadio:1)}
When specifying a supported data model and its version, the profile version tested will be the most recent version which was included in the minor version specified. This means that values like this:
testvar uspSupportedDataModel {Device:2.1[](Baseline:3)}
will skip the baseline profile because the 3rd version of the Baseline profile did not exist in version 2.1 of the Device data model.
USP Parameter Data Validation
By default, CDRouter will perform data validation on USP profile parameters.
To disable data validation, set uspDataValidation to no.
When data validation is enabled, CDRouter will verify that the value of every
parameter is syntactically correct according to syntax information contained
within the Broadband Forum’s official XML data model definitions. If a
parameter fails data validation, CDRouter will print a message detailing why the
parameter’s value is incorrect and the test will fail.
Custom USP Profiles
CDRouter supports user defined profiles. To test a user defined profile, set the
testvar uspProfileName to the name of the profile you would like
to test and uspProfilePath to the unix file path to the XML file
containing profile.
Note: in CWMP profile testing, there is support for specifying profiles in XML format as well as QA Cafe’s proprietary format. The proprietary format is not available as a file format for USP profile testing.
To then test this custom profile, after setting the testvars, run
the usp_datamodels.tcl test module.
Example config:
testvar_group usp_profile_1 {
testvar uspProfileName STOMPHeartbeats:1
testvar uspProfilePath /usr/cdrouter-data/custom/my-usp-profile.xml
}
It is also possible to set the uspProfilePath testvar to “auto”.
When set to this value, CDRouter’s controller will issue a GetSupportedDM message
to the agent in start targeting the root object. The response from the agent
will be treated as one large profile which will be used in the usp_datamodels.tcl
test module. Additionally when uspProfilePath is set to “auto”
CDRouter will save the extracted data model to the result’s log directory. The
data model will be saved as “usp-extracted-data-model.xml” in the BBF data model
XML format, which can then be used as a custom data model in subsequent test runs.
It’s important to remember that the extracted data model is entirely based on the
reported data model from the agent. The extracted data model should be used as a
starting point and should not be interpreted as the complete data model the agent
was expected to implement.
Excluding USP Parameters
In some cases, you may wish to exclude a parameter from the USP profile check
because it is not supported by the device under test. CDRouter allows you do to
this by configuring a list of parameters to skip in the uspSkipParameters
testvar. A list of parameters can be specified by
enclosing the list members between “{“ and “}”. The list of parameters can be
either full instances or generic instances that use “{i}” for each instance
index. Note that each individual parameter within the list must be specified
using a full instance or partial path, or a fully generic instance using “{i}”
for each index. Parameters cannot be specified using a mix of generic and full
instances. Here is an example:
testvar uspSkipParameters {
Device.DeviceInfo.ModelName
Device.USP.InterfaceNumberOfEntries
}
If you are skipping an entire object path and all parameters contained below it,
you only need to specify the top object path. All top object paths (partial
paths) must end with a ‘.’ character. For example, if the device under test does
not support the Stats object from a PTM link, you
could skip the object by configuring the following uspSkipParameters
testvar:
testvar uspSkipParameters {
Device.PTM.Link.{i}.Stats.
}
Modifying USP Parameters
All USP profiles supported by CDRouter and their corresponding objects and
parameters are defined in the /usr/cdrouter/tests/usp-profiles directory.
The type, requirement, or syntax of any of these pre-defined objects and
parameters can be modified using the uspModifyParameters
testvar. Like the uspSkipParameters testvar uspModifyParameters
supports a list.
When modifying parameters we recommend copying the original parameter definition
from the /usr/cdrouter/tests/usp-profiles directory and then making the
required modifications using uspModifyParameters. Here is an
example that modifies the enumeration syntax of the
Device.DSL.BondingGroup.{i}.Status
parameter to support the additional keywords of auto and foo:
testvar uspModifyParameters {
string R Device.DSL.BondingGroup.{i}.Status {enumeration {Up Down NotPresent LowerLayerDown}}
}
Likewise, here is an example that changes the requirement of the
Device.Time.NTPServer1 parameter from write, W, to read-
only, R:
testvar uspModifyParameters {
string R Device.Time.NTPServer1 {size {maxLength 64}}
}
Note that the syntax argument is optional when modifying parameters. If omitted CDRouter will only overwrite the type and requirement for the specified parameter. As a result the above example can be reduced to this:
testvar uspModifyParameters {
string R Device.Time.NTPServer1
}
USP Software Module Management (SMM) Testing
CDRouter’s USP expansion contains a module of test cases to help validate Software Module Management functionality for USP agent implementations.
Typically, in these test cases, CDRouter simulates a USP Controller that instructs the agent to download a software module from a location (URL) that exists on a server separate from the CDRouter system.
In shared test setups, where there is a shared termination device (CMTS, OLT, etc.) that is inbetween the DUT and CDRouter’s WAN connection, the DUT can directly connect to that URL on the separate server.
In closed-loop test setups, where the DUT’s WAN is directly connected to CDRouter’s WAN port, the DUT can only reach the URL on a separate server by routing traffic through CDRouter. These test setups require the use of CDRouter’s Internet Connection Service (ICS) feature.
Alternatively, if the test setup does not have a separate server to store software modules, CDRouter’s built-in HTTP server may be able to be used to serve the required software modules.
The following section provides an example of how to do this -
Setup General Purpose HTTP Server
Example configuration of HTTP Server -
SECTION "General Purpose HTTP Server" {
testvar httpServerIp 3.3.3.16
testvar httpServerPort 80
testvar httpServerRoot /usr/cdrouter-data/custom
}
Configure USP Software Module Management Section
After successfully configuring the general purpose HTTP server, configure the “USP Agent Software Module Management” section of the CDRouter configuration file to make use of the HTTP Server.
Note that the values for the URL testvars specify the IP of the general purpose HTTP server.
SECTION "USP Agent Software Module Management" {
testvar uspSoftwareModuelURL http://3.3.3.16/<module filename>
testvar uspSoftwareModuleUpdateURL http://3.3.3.16/<other module filename>
testvar uspSoftwareModuleUsername anonymous
#testvar uspSoftwareModulePassword qacafe123
testvar uspSoftwareModuleUUID 01234567-890a-bcde-f012-3456789abcde
#testvar uspSoftwareModuleEEName default
#testvar uspSoftwareModuleEEClassName default
testvar uspSoftwareModuleTimeout 120
}
The module files will need to be copied over to the CDRouter system and
placed into the directory specified by the httpServerRoot.
Broadband Forum USP Agent Certification
CDRouter is the official test tool of the Broadband Forum’s USP Agent Certification program. CDRouter includes a full implementation of TP-469 Conformance Test Plan for USP Agents in the usp_conformance test module.
More information on how to use the CDRouter USP Expansion to perform self-testing certification can be found here.
Troubleshooting
Controller is not sending messages
Agent IP configuration
Before the controller will send any USP messages, it will ARP for the agent’s IP. If the agent doesn’t have the correct IP address it will never respond to the ARPs being sent. If the agent is configured to use a static IP ensure it matches what is in the config file. If the agent is configured to get an IP via DHCP, ensure the agent IP address in the config file is either set to “auto” or the DHCP pool is configured to allow for one address and that the appropriate agent IP testvar is set to that address.
If STOMP is being used as the MTP and the agent is getting an IP address but the
controller is not sending any messages, ensure the agent is correctly connecting
to the STOMP server and subscribing to the correct destination. The controller
will not attempt to send any messages until the agent has correctly connected
and subscribed to the right destination on the STOMP server. If the agent
appears to be attempting to connect to the STOMP server ensure the uspControllerUsername
and uspControllerPassword are
correctly set to the credentials the agent provides.
Agent not responding to USP messages
If the controller is sending USP messages to the agent’s IP address and not getting a response ensure the following are correctly configured:
- The MTP the controller is using matches what the agent is expected to use.
- The port used to accept connections on the agent is correctly configured in the config file.
uspControllerIDmatches what the agent expects the controller ID to beuspAgentIDmatched the endpoint ID configured on the agentuspControllerUseSessionContextis set to “yes” if the agent is expected to use a session context
Agent’s responses are ignored by the controller
If the controller is ignoring the responses the agent is sending ensure:
uspControllerIDmatches theto_idin the agent’s responsesuspAgentIDmatches thefrom_idin the agent’s responses- The
message_idof the message sent to the agent matches themessage_idin the agent’s response
Other Issues
TLS
If USP payload security is configured it’s possible there is an issue with the certificate exchange or with the fact that there might be more than one TLS record in a single message.
Controller is dropping messages
If the controller cannot properly decode messages it receives from the agent it will issue a warning in the log and drop it. The most likely reason for a message to not decode properly is an issue with the protobuf encoding.
Reboot Tests
Tests usp_conformance_6_7, usp_conformance_6_10, usp_conformance_11_10, and
usp_conformance_11_12 require that the DUT be rebooted by a mechanism
other than USP. Use RestartDut and cpeRebootMode
to configure the DUT to be rebooted automatically or manually with a prompt.
See the
CDRouter User Guide
for more information.
-
NOTE: Replace
{i}with the specific instance number of your agent’s parameters ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ -
NOTE:
STOMP.Referenceparameters must reference the same instance ofDevice.STOMP.Connection.{i}.Unencrypted Connection ↩︎ ↩︎ -
NOTE:
MQTT.Referenceparameters must reference the same instance ofDevice.MQTT.Client.{i}.Unencrypted Connection ↩︎ ↩︎